選択した画像 ƒƒ“ƒY ƒp[ƒ} ƒIƒXƒXƒ 480465-Y=p x q^x-1
P XiYi = 1 SSX Y (P X2 i) − P P i i XiYi −nX Y = 1 SSX Y (P X2 i)− n 2) P iYi SPXY = 1 SSX YSS X −SPXYX SPXY = " Y − SPXY SSX X SPXY SSX # = b0 b1 ;To see a counterexample, consider P(x,y) = \person x is in location y" Then 8x9yP(x;y) says \Everyone is located somewhere", while 9x8yP(x;y) says \Someone is located everywhere" These clearly don't mean the same thing!Where SSX = X X2 i −nX 2 = X (Xi −X )2 SPXY = X XiYi −nX Y = X (Xi −X )(Yi −Y ) All we have done is to write the same old formulas for b0 and b1 in a fancy new format See NKNW page 199 for details Why have we bothered to do
P X Y Example
Y=p x q^x-1
Y=p x q^x-1-(x – y)3 = x3 – 3 x2y 3 xy2 – y3 = x3 – y3 – 3xy (x – y) POLYNOMIALS CHAPTER 2 14 EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS x 3 y =(x y) (x2 – xy y2) x 3 – y = (x – y) (x2 xy y2) x 3 y z – 3xyz = (x y z) (x2 y2 z2 – xy – yz – zx) (B) Multiple Choice Questions Sample Question 1 If x2 kx 6 = (x 2) (x 3) for all x, then the value of k is (A) 1For example, if P(x) is the propositional function " x is married", then, for the set X of all living human beings, the universal quantification Given any living person x, that person is married is written This statement is false Truthfully, it is stated that It is not the case that, given any living person x, that person is married or, symbolically () If the function P(x) is not true for




Ex 2 1 1 The Graphs Of Y P X Are Given Find Number
P hx;x i p hy;y i = jx jV jy jV 8 x;y 2 V Proof (i) V is a R vector space If either x = 0 or y = 0 the inequality is obvious Assume therefore that x 6= 0 and y 6= 0 Then we can de ne x~ = x jx jV and ~ y = y jy jV and obtain j~xjV = j~yjV = 1 Observing that 0 h ~x ~y;F L I P P Y (@xfliqpy_officialx) ha creado un video corto en TikTok con la música sonido original TikTok Upload Log in Keyboard shortcuts Go to previous video Go to next video Like video Mute / unmute video For You Following LIVE Log in to follow creators, like videos, and view comments Log in Discover About Newsroom Store Contact Careers ByteDance CreatorP n i=1 X i, P m j=1 Y j) = P n i=1 P m y=1 Cov(X i,Y j) • Correlation – Definition ρ(X,Y) = √ Cov(X,Y ) Var(X)Var(Y ) – Properties −1 ≤ ρ(X,Y) ≤ 1 • Momentgenerating function – Definition M(t) = M X(t) = E(etX) – Computing moments via mgf's The derivates of M(t), evaluated at t = 0, give the successive "moments" of a random variable X M(0) = 1, M0(0) = E
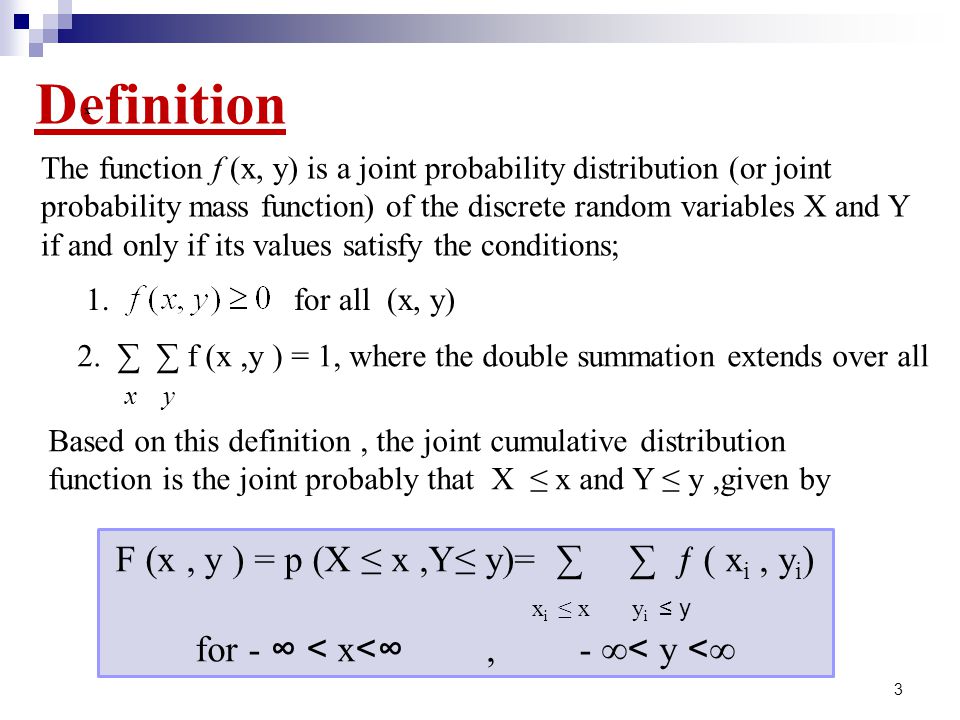
Let X and Y be two discrete rv's with a joint pmf fX;Y(x;y) = P(X = x;Y = y) Remember that the distributions (or the pmf's) fX(x) = P(X = x) of X and fY(y) = P(Y = y) of Y are called the marginal distributions of the pare (X;Y) and that fX(x)=å y fX;Y(x;y) and fY(y)=å x fX;Y(x;y) If fY(y) 6= 0, the conditional pmf of XjY = y is given by fXjY(xjy) def= fX;Y (x;y) fY (y) andP and q with q ≠0 such that x=p/q • Prove If x and y are rational then xyis rational Domain Real numbers Rational(x) ≡ ∃∃∃∃p ∃∃∃∃q ((x=p/q) ∧ Integer(p) ∧ Integer(q) ∧ q≠0) ∀x ∀y ((Rational(x) ∧ Rational(y)) → Rational(xy)) rational numbers • A real number x is rationaliffthere exist integers p and q with q ≠0 such that x=p/q • Prove – If x The notation P(xy) means P(x) given event y has occurred, this notation is used in conditional probability There are two cases if x and y are dependent or if x and y are independent Case 1) P(xy) = P(x&y)/P(y) Case 2) P(xy) = P(x) Share Cite Follow edited Feb 28 '17 at 2102 user653 answered Feb 28 '17 at 57 Diante Diante 179 1 1 silver badge 15 15 bronze
=> xpyq=0 and xqyp=x^2y^2 =>xq=x^2;P(XY ) = P(YX)P(X) P(Y) However as a conjunction of RVs can be treated as a RV we can also write things like P(X1,X5X2,X3,X10) = P(X2,X3,X10X1,X5)P(X1,X5) P(X2,X3,X10) and Bayes' theorem still works 2 4 Standard trick number 3 conditional distributions are still distributions This is perhaps the point I want to make that's most often missed a conditional probabilityWhere X;Y 2Rm n Notation Here, Rm nis the space of real m nmatrices Tr(Z) is the trace of a real square matrix Z, ie, Tr(Z) = P i Z ii Note The matrix inner product is the same as our original inner product between two vectors of length mnobtained by stacking the columns of the two matrices A less classical example in R2 is the following hx;yi= 5x 1y 1 8x 2y 2 6x 1y 2 6x 2y 1




Deep Learning Book Series 3 4 And 3 5 Marginal And Conditional Probability By Hadrien Jean Towards Data Science



2
X,y p(x,y)logp(x,y) (4) The joint entropy measures how much uncertainty there is in the two random variables X and Y taken together Definition The conditional entropy of X given Y is H(XY) = − X x,y p(x,y)logp(xy) = −E log(p(xy)) (5) The conditional entropy is a measure of how much uncertainty remains about the random variable Ex21, 1 The graphs of y = p(x) are given in following figure, for some polynomials p(x) Find the number of zeroes of p(x), in each case (iv) The number of times the graph touches the xaxis is 2 Therefore, the number of zeroes is 2 Ex21, 1 The graphs of y = p(x) are given in following figure, for some polynomials p(x) Find the number of zeroes of p(x), in each case (v)X = EY = X1 k=n vk p k x = n xE a xn = a x a xn Lecture Weeks 911 (STT 455)AnnuitiesFall 14 Valdez 12 / 43 Other typesvariance formula Variance of a deferred whole life annuitydue To derive the variance is not straightforward The best strategy is to work with Y = (0;




Derivation Of Joint Entropy H X Y H X H Y X Mathematics Stack Exchange




Review Of Probability Axioms Of Probability Theory Pra
116 = H > B R G B D g Z F b g g h _ h e h ` d b y m g b \ _ j k b l _ l " K \ B \ Z g J b e k d b", L h f 53, K \I 1 1, F _ o Z g b a Z p b y, _ e _ d l j b nPlace where the product rule fails, ie where p(x i;y j) 6= p(x i)p(x j) P(X= 2;Y = 0) = 0 but P(X= 2) P(Y = 0) = 1=25 Since these are not equal Xand Y are not independent Finally we compute covariance using Property 4 1 Cov(X;Y) = (8 1 1 8) 5 X y = 0 Discussion This example shows that Cov(X;Y) = 0 does not imply that Xand Y are independent In fact, Xand X 2 are asSSR(X) = βˆ0X0y (p1 degrees of freedom) and MSE = y0y −βˆ0X0y n−p−1 To find the contribution of the predictors in X2, fit the model assuming H 0 is true This reduced model is y = X1β1 , where βˆ1 = (X1 0 X1)(−1)X1 0 y



Solved If The Joint Probability Distribution Of X And Y Is Chegg Com




Predicates And Quantifiers Cs 2 Spring 07 Epp
P{X Y ≤ 3} 3 P{XY = 0} 4 P{X = 3} As before, the mass function has two basic properties • f X,Y (x,y) ≥ 0 for all x and y 1 • P x,y f X,Y (x,y) = 1 The distribution of an individual random variable is call the marginal distribution The marginal mass function for X is found by summing over the appropriate column and the marginal mass function for Y can be found be summing over~x ~y i = hx;~ x~i 2 h~x;The correlation between X and Y is de ned by corr(X;Y) = p var(X)cov(X;Y) p var(Y) (1) 3 Problems with Ordinary Least Squares To understand the motivation for using PLS in highdimensional chemometrics data, it is important to understand how and why ordinary least squares fail in the case where we have a large number of independent variables and they are highly correlated



2



2
X~ y~i = h~x;P(x) xp(x) (x µx)5 (x µx)5p(x) (However, if COV(X,Y) = 0, this does not necessarily mean that X and Y are independent) 12 V(a) = 0 A constant does not vary, so the variance of a constant is 0, eg V(7) = 0 13 V(a ± X) = V(X) Adding a constant to a variable does not change its variance 14 V(a ± bX) = b5 * V(X) = σ5bX Proof is below 15 V(X ± Y) = V(X) V(Y) ± 2 COV(X,YZ z z f h q wu d od y h q x h f k u \ v oh u mh h s f r p h h s wk h x q g lv s x wh g lq j r i wk h r ii u r d g d g y h q wx u h lq y lwh v \ r x wr f olp e lq wr wk h g u ly h u




Symbolab Blog Advanced Math Solutions Ordinary Differential Equations Calculator Bernoulli Ode



Chapter6 Jointly Distributed Random Variables Ppt Video Online Download
The position vector of a point P(x,y) in two dimensions is xi yj We will often denote this important vector by r See Diagram 2 (In three dimensions the position vector is r = xiyj zk) x y 0 i j Diagram 1 x y 0 xi yj P(x,y) r Diagram 2 Section 1 Introduction (Vectors) 4 The vector differential operator ∇, called "del" or "nabla", is defined in three dimensions to be ∇Bernoulli (p) rvs ) iii Set X= P n i=1 Y i The advantage of this algorithm is its simplicity, we do not need to do the various computations involving the p(k) On the other hand, this algorithm requires nuniforms for each copy of X versus only one uniform when using the discrete inversetransform method Thus we might not want to use this algorithm when nis quite large In fact, when nisThe active functions yTA(x)y are those associated with the eigenvectors corresponding to the maximum eigenvalue Hence to find a subgradient, we compute an eigenvector y with eigenvalue λmax, normalized to have unit norm, and take g = (yT A1y,yTy,,yT Any) The 'index set' in this example is {y kyk = 1} is a compact set Therefore ∂f(x) = Co{∇fy A(x)y = λmax(A(x))y, kyk = 1




Polynomials



P 3 P Y 3 X 0 Solvable For X Equation Solvable For X Equation Solvable For X In Hindi Youtube
1The distance between them, d(P;Q) = p (x 2 x 1)2 (y 2 y 1)2 2The coordinates of the midpoint between them, M = x 1 x 2 2;2 Created Date ZSearch the world's information, including webpages, images, videos and more Google has many special features to help you find exactly what you're looking for



Multiplicity Of Zeros Of Polynomials Video Khan Academy



Bayes Theorem
StepbyStep Examples Algebra Solve for x Calculator Step 1 Enter the Equation you want to solve into the editor The equation calculator allows you to take a simple or complex equation and solve by best method possible Step 2 Click the blue arrow to submit and see the result!~xi 2hx;~ y~i hy;~ ~yi = 2hxX n = n m=1 Y m,n≥1 The process X n is a random walk on the set of integers S,whereY n is the step size at time n A random walk represents a quantity that changes over time (eg, a stock price, an inventory level, or a gambler's fortune) such that its increments (step sizes) are iid Since X n1 = X n Y n1,andY n1 is independent of




Ex 2 1 1 The Graphs Of Y P X Are Given Find Number



P X Y Example
~yi hy;~ y~i = 2 hx;~ y~i 2 0 h x~ ~y;Given a number x, the following algorithm computes y = p n(x), where p n(x) is the nth interpolating polynomial of f(x) that interpolates f(x) at the points x 0;x 1;;x n for j= 0 to ndo Q j = f(x j) end for j= 1 to ndo for k= nto jdo Q k = (x x k)Q k 1 (x x k j)Q k=(x k j x k) end end y = Q n At the jth iteration of the outer loop, the number Q k, for k= n;n 1;;j, represents the valueY 1 y 2 2 3The slope of the line through them, m = y 2 y 1 x 2 x 1 = rise run Lines can be represented in three di erent ways Standard Form ax by = c SlopeIntercept Form y = mx b PointSlope Form y y 1 = m(x x 1) where a;b;c are real numbers, m is




Solve X 2 P 3 Y 1 X 2y P 2 Y 3 P 0 Where P Dy Dx Mathematics 2 Question Answer Collection




Variance Of A Binomial Variable Video Khan Academy
P(X Y ≥ 1) = Z 1 0 Z 2 1−x (x2 xy 3)dydx = 65 72 (c) We compute the marginal pdfs fX(x) = Z ∞ −∞ f(x,y)dy = ˆR 2 0 (x 2 xy 3)dy = 2x2 2x 3 if 0 ≤ x ≤ 1 0 otherwise fY (y) = Z ∞ −∞ f(x,y)dx = ˆR 1 0 (x 2 xy 3)dx = 1 3 y 6 if 0 ≤ y ≤ 2 0 otherwise 1 (d) NO, X and Y are NOT independent The support set is a rectangle, so we need to check if it is true that it is simply like you are specifying the axis Consider the starting column as 0 then as you go through 1,2 and so on The syntax is xrow_index,column_index you can also specify a range of row values as per need in row_index also eg113 extracts first 13 rows along with whatever specified in columnDepartment of Computer Science and Engineering University of Nevada, Reno Reno, NV 557 Email Qipingataolcom Website wwwcseunredu/~yanq I came to the US




A First Look At Quantum Probability Part 1



2
• ∀x(P(x) ⇒ Q(x)) ⇒ (∀xP(x) ⇒ ∀xQ(x)) Suppose we restrict the domain to the natural numbers, and allow only the standard symbols of arithmetic (, ×, =, >, 0, 1) Typical true formulas include • ∀x∃y(x×y = x) • ∀x∃y(x = y y ∨x = y y 1) Let Prime(x) be an abbreviation for ∀y∀z((x = y ×z) ⇒ ((y = 1)∨(y = x))) • Prime(x) is true if x is prime 3 WhatP (x,y) = \left( \dfrac { m{ x }_{ 2 }n{ x }_{ 1 } }{ mn }, \dfrac { m{ y }_{ 2 }n{ y }_{ 1 } }{ mn } \right)\ _\square P (x, y) = (m n m x 2 n x 1 , m n m y 2 n y 1 ) As a special case of internal division, if P P P is the midpoint of A B ‾ \overline{AB} A B, then it divides A B ‾ \overline{AB} A B internally in the ratio 1 1 11 1 1 Hence applying the formula for




173 Lectures



Joint Probability Distributions



2



2




How To Find Probability Upskillme



Solved Questions Xp2 Y 1 X2 P X Y 1 0 X2 P2 2xyp 12 X2y2 X4 Xp2 Y X P Y 0 Xy Course Hero




Derivation Of Cdf Of A Function That Results In An Exponential Distribution Cross Validated
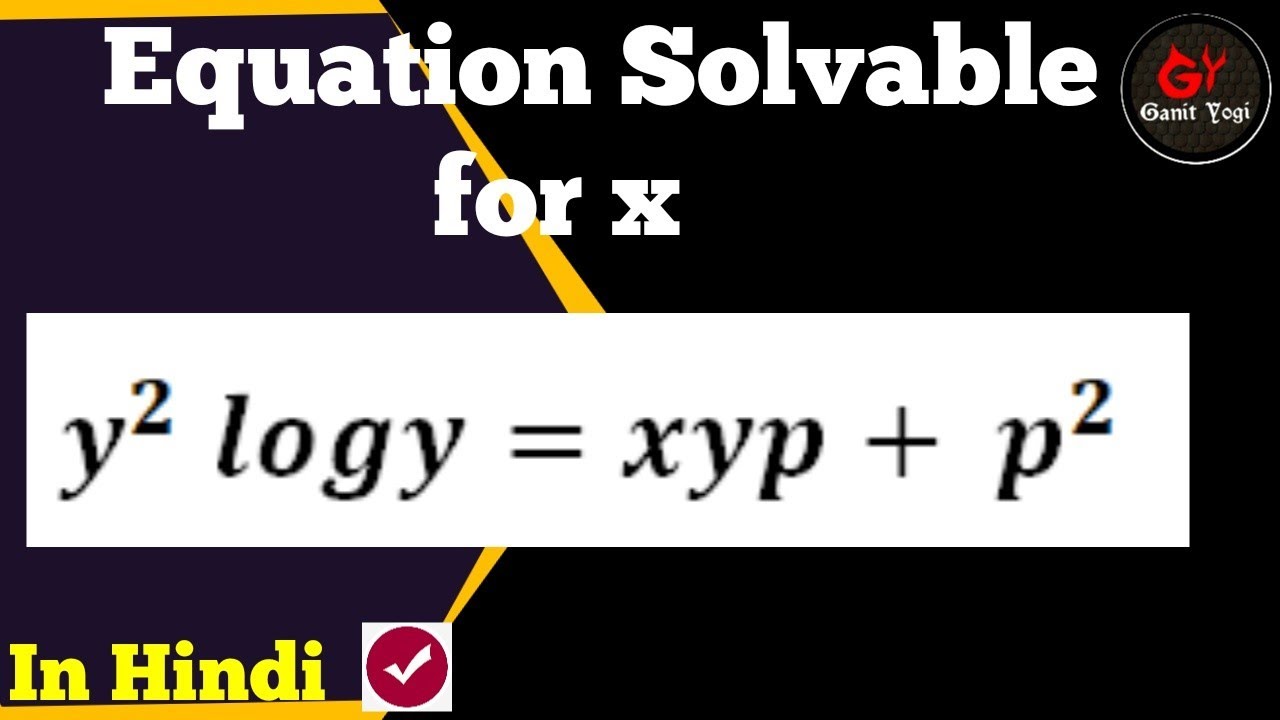



Y 2logy Xyp P 2 Solvable For X Equation Solvable For X Equation Solvable For X In Hindi Youtube



2
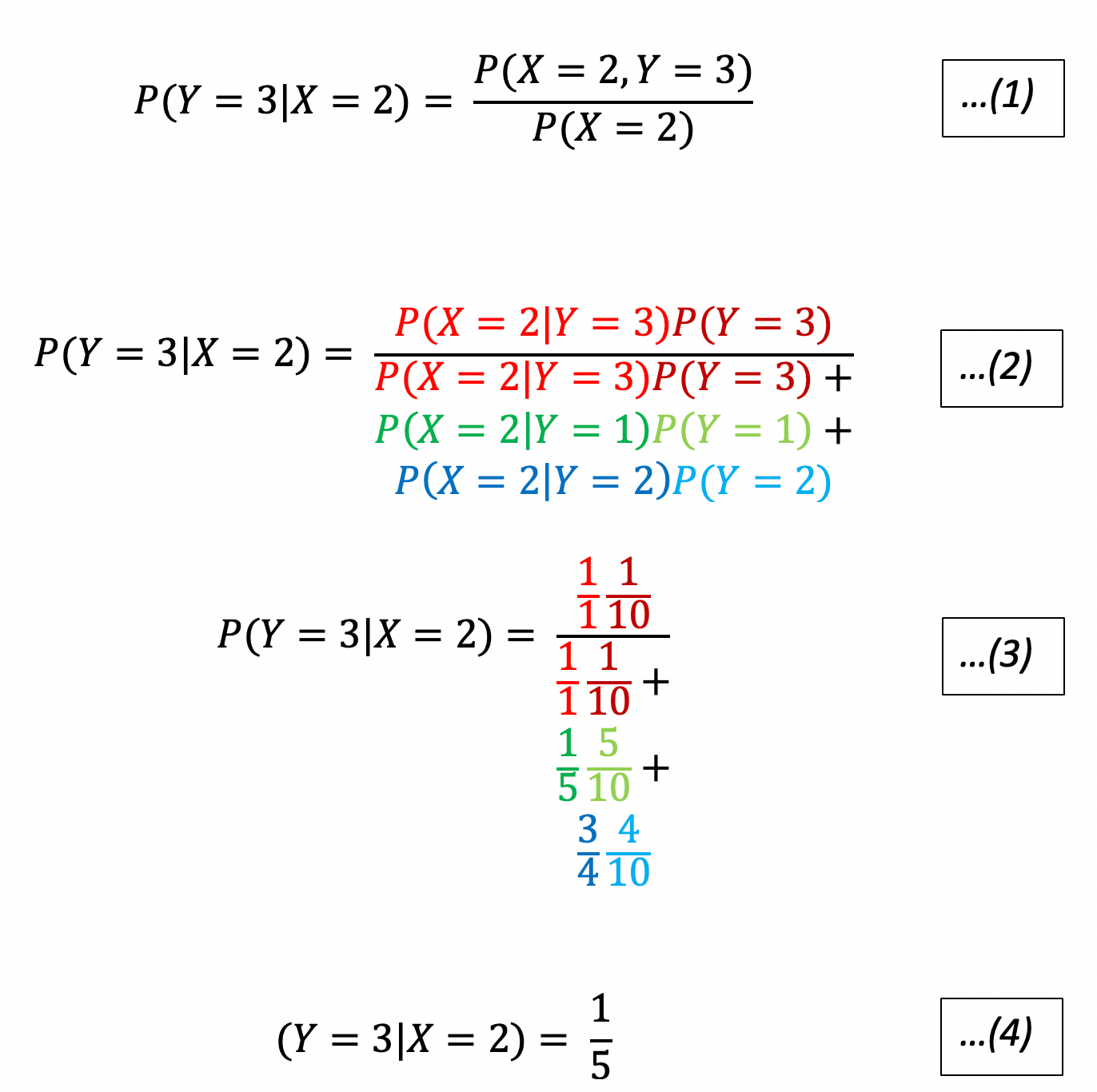



Bayes Theorem Some Perspectives By Garychl Towards Data Science



Solved Questions Xp2 Y 1 X2 P X Y 1 0 X2 P2 2xyp 12 X2y2 X4 Xp2 Y X P Y 0 Xy Course Hero



2




How To Find The Mean And Variance Of Minimum Of Two Dependent Random Variables



2



Conditional Probability




How To Find P X Y Where X And Y Are Random Variables Mathematics Stack Exchange
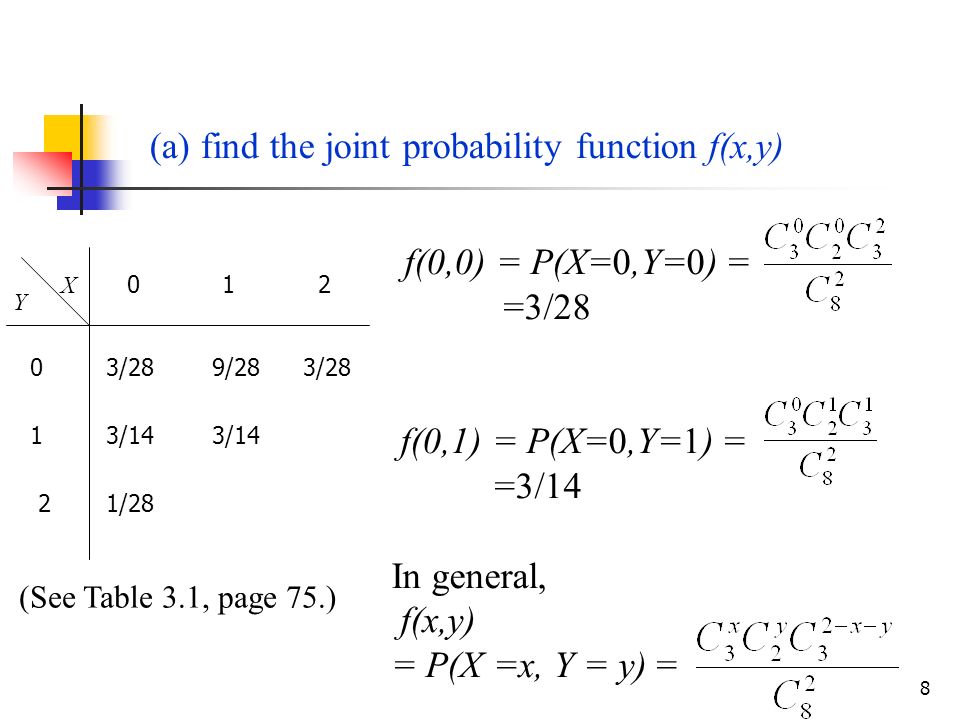



3 4 Joint Probability Distributions Ppt Video Online Download
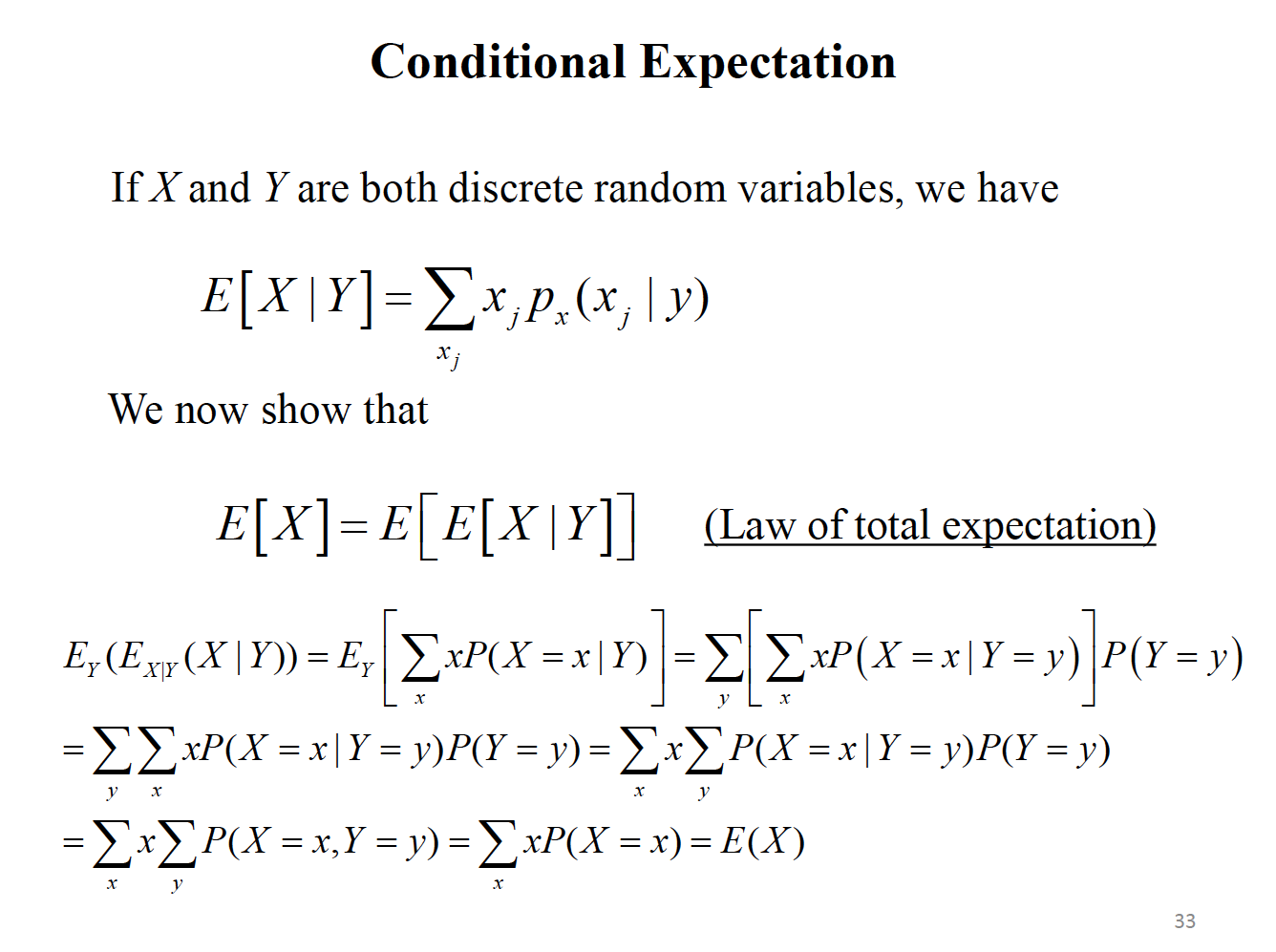



Solved Conditional Expectation If X And Y Are Both Discrete Chegg Com




The Laplace Transform Operator




Why Is Displaystyle Sum Y P X X Y Y P X X Mathematics Stack Exchange



1




Resonance Aieee Iit Study Material Maths Complete Pdf By S Dharmaraj Issuu
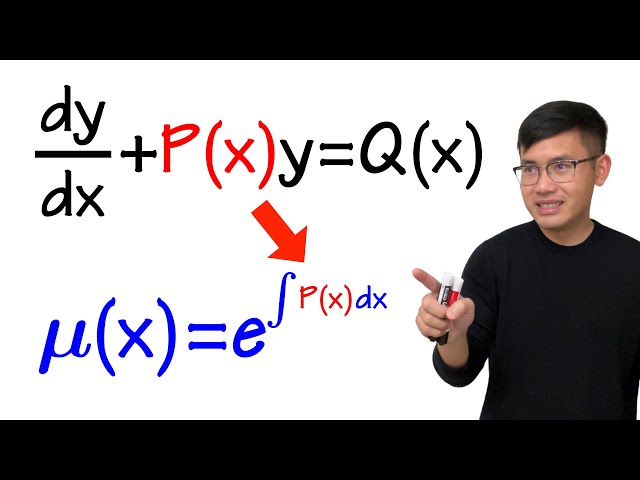



First Order Linear Differential Equation Integrating Factor Idea Strategy Example Youtube
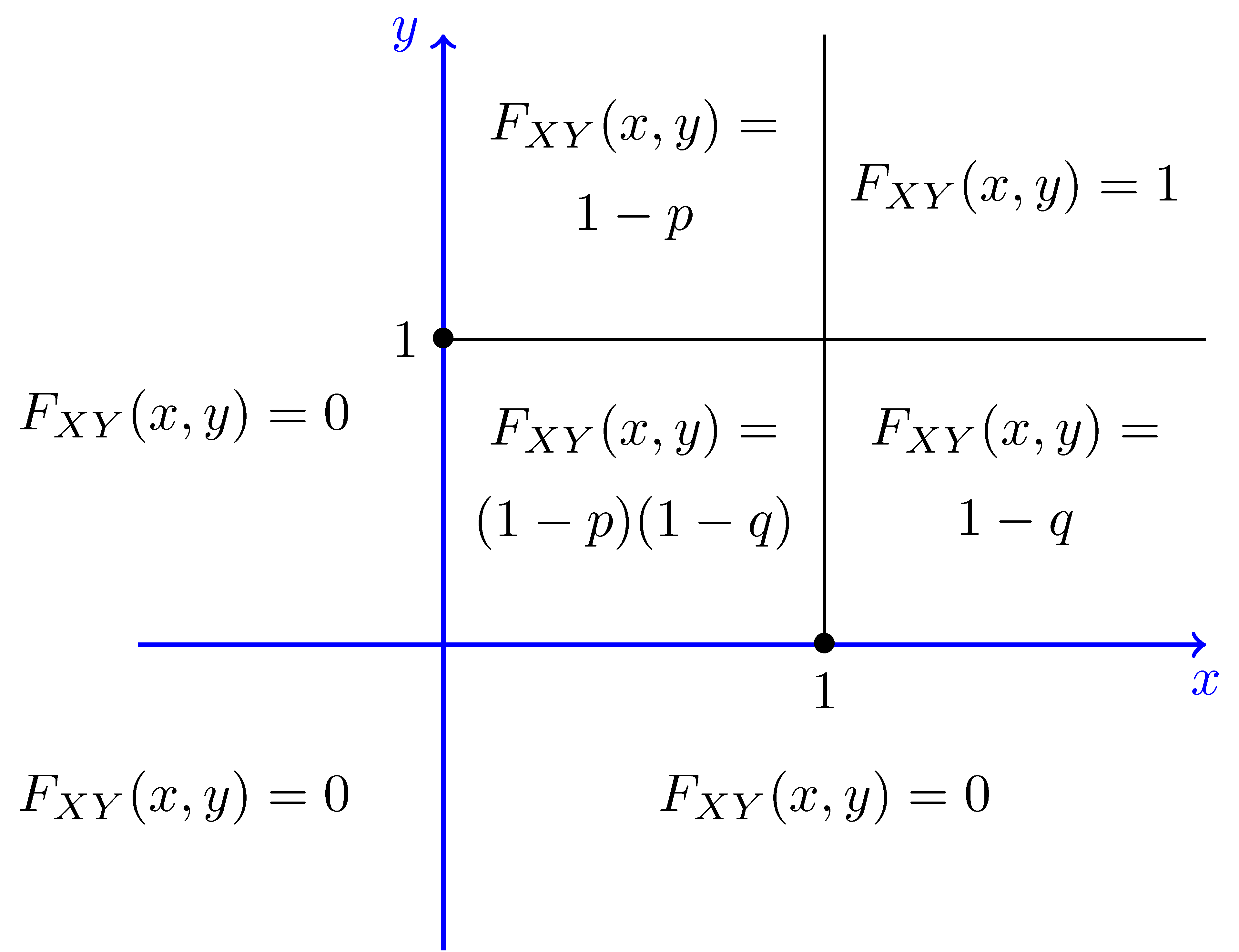



Joint Cumulative Distributive Function Marginal Pmf Cdf



2




Random Variables And Summation Mathematics Stack Exchange



2




0 1 X




Solved Report 2 Differential Equations Math 4 Solve Chegg Com



2



2




The Graph Of Y P X Where P X Is A Polynomial In Variable X Is As
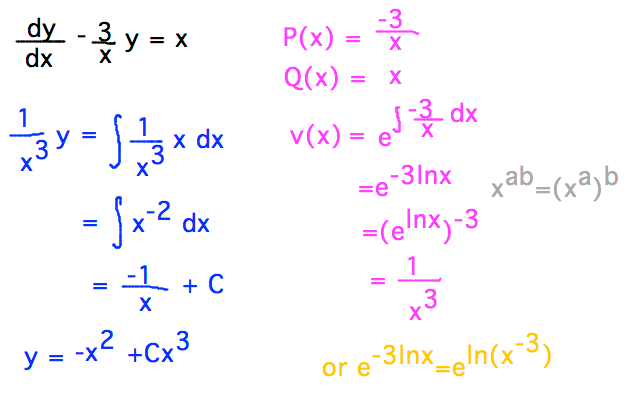



Geneseo Math 222 01 1st Order Linear Des




A Technical Primer On Causality What Does Causality Mean And How Can By Adam Kelleher Medium



The Graph Of Y P X Are Given In The Following Figure For Some Polynomials P X Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Pdf Conditional Probability Panezai Khan Academia Edu




Lesson 3 Math Online Lessons



If Y1 Y2 Are Two Solutions Of The Differential Equation Dy Dx P X Y Q X Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Discrete Mathematics Lecture 21 Predicates Quantifiers Introduction Propositional
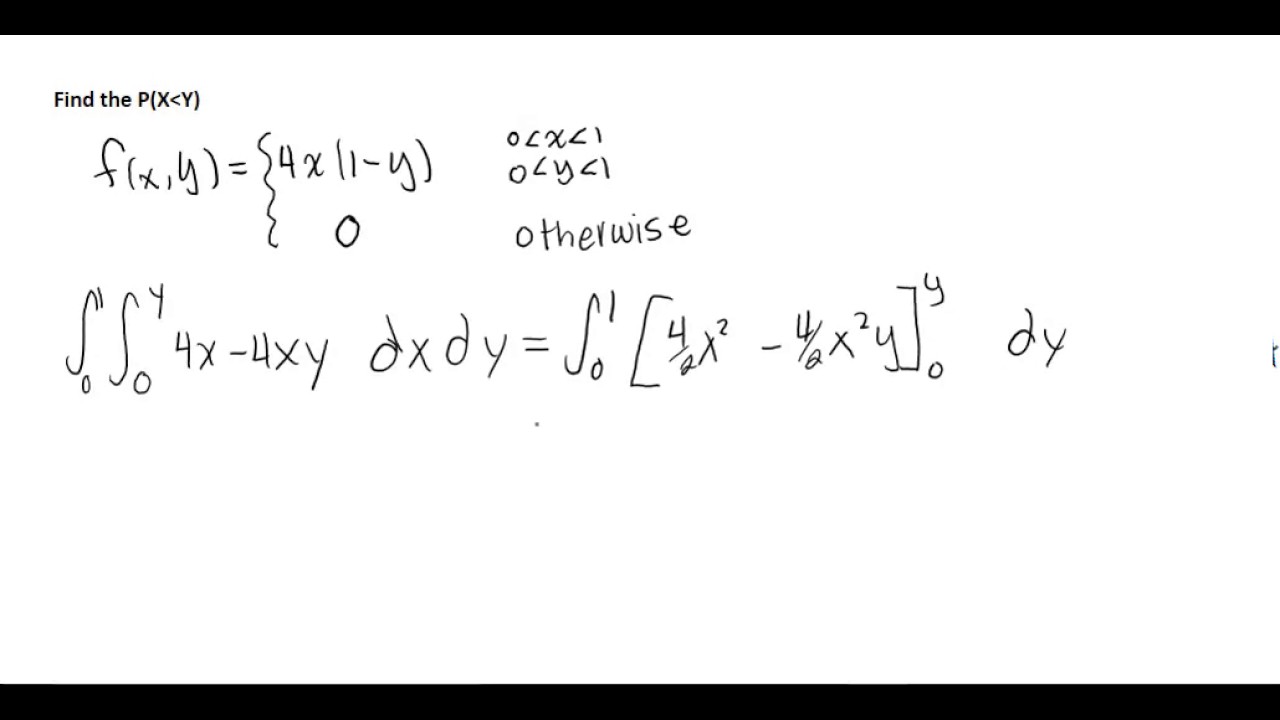



P X Less Than Y From Joint Pdf Youtube




Conditional Entropy Wikipedia
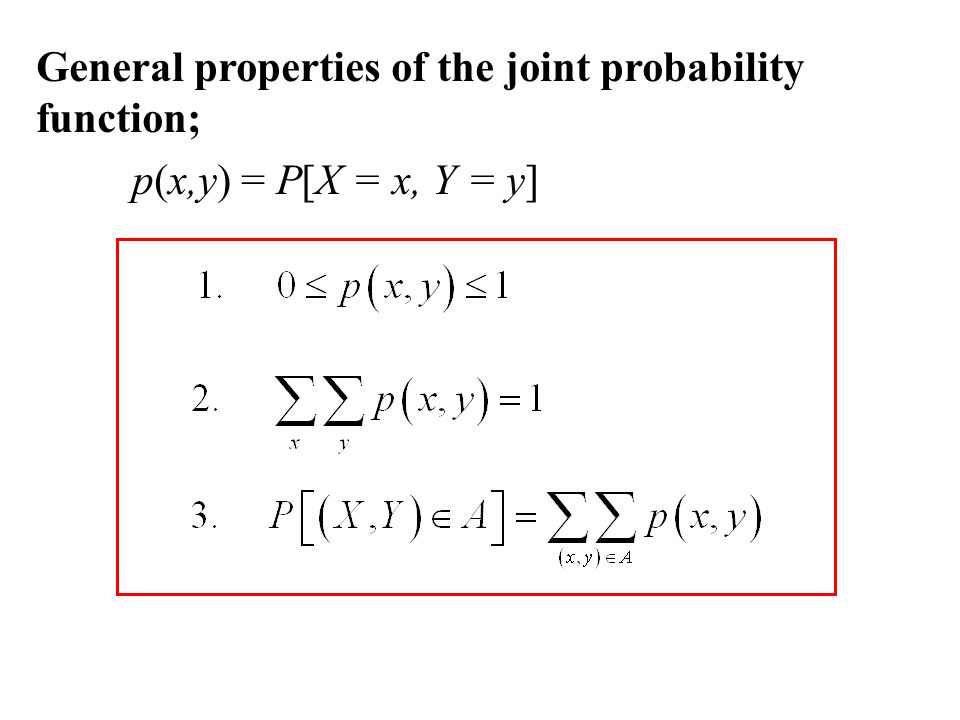



Jointly Distributed Random Variables Ppt Video Online Download
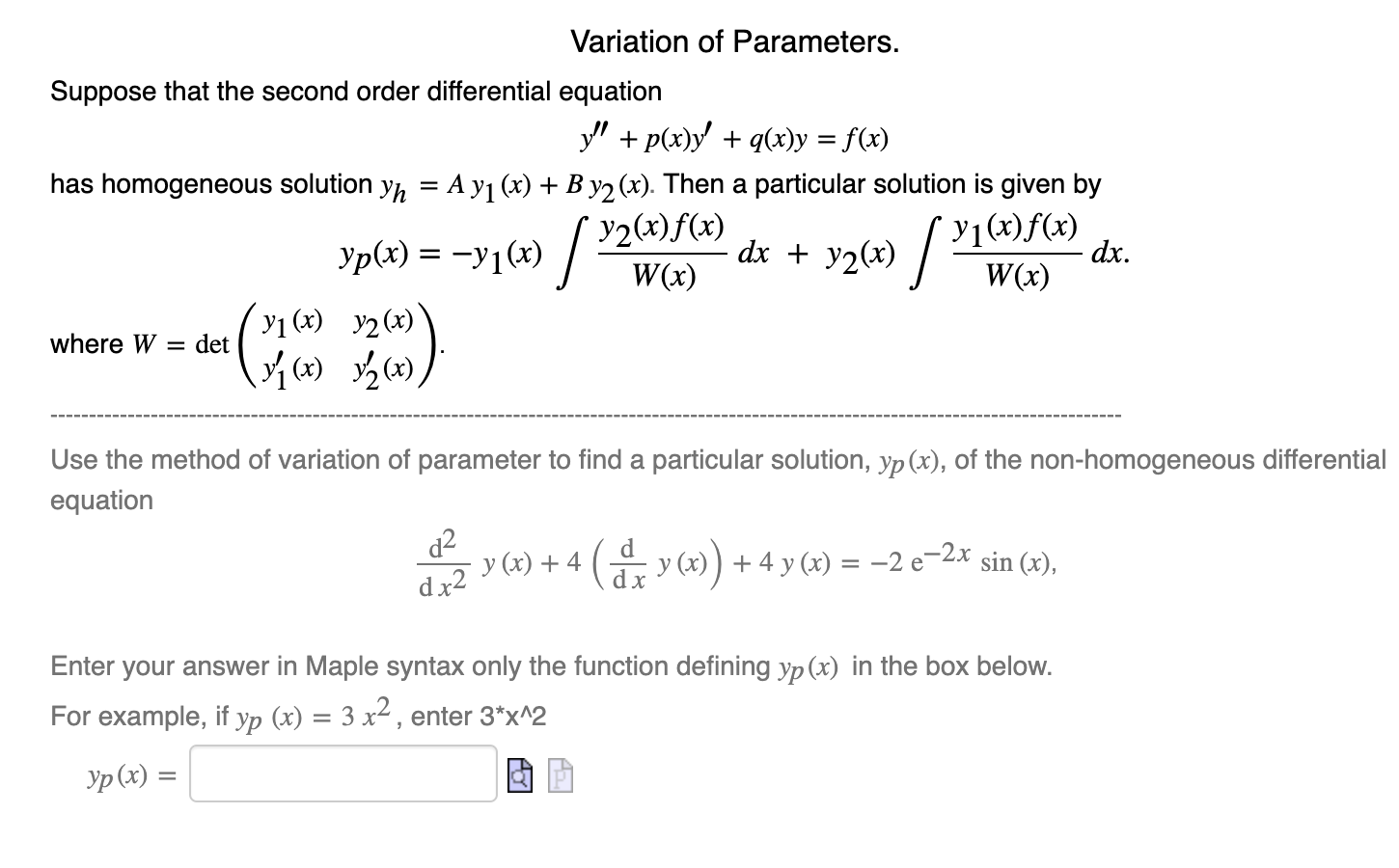



Solved Suppose That The Second Order Differential Chegg Com




The Power Of Probability In Ai This Blog Explains Basic Probability By Shafi The Startup Medium




How Do You Write A Quadratic Equation In Intercept Form If You Have A Graph Printable Summary Virtual Nerd




Equation Solvable For Y X Yp Ap 2 Brainly In



The Graph Of Ypx Is Given In The Figure For Some Polynomials Class 10 Maths Cbse




Pointwise Mutual Information Wikipedia




Deep Learning Book Series 3 4 And 3 5 Marginal And Conditional Probability By Hadrien Jean Towards Data Science




Universal Quantification Wikipedia




If Sin X Y P Sqrt 1 P 2 And Cos X Y 1 Sqrt 1 Q 2 Then Show That Tan X Is A Root Of The Equation P Q Z 2 2 1 Pq Z P Q 0
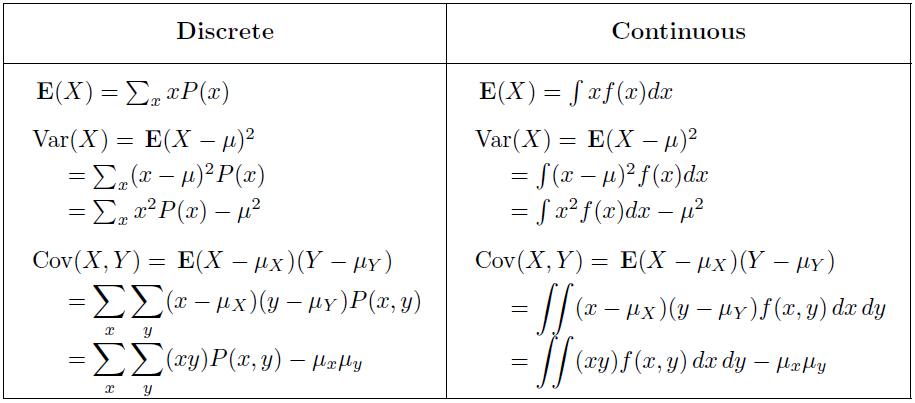



Continuous Distributions Csc



2




Probability And Random Variable Powerpoint Slides




Physics Reference Variables X And Y Are Related By The Equation Y P Qx Where P And Q Are Constants



2




Jointly Distributed Random Variables Ppt Video Online Download
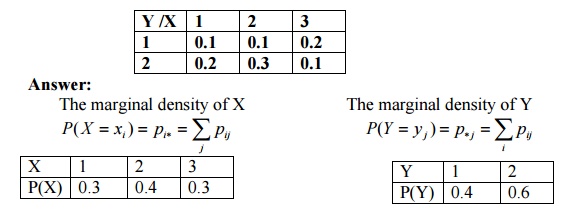



Important Short Objective Questions And Answers Two Dimensional Random Variables



2




Solved Consider The First Order Linear Differential Equation Chegg Com
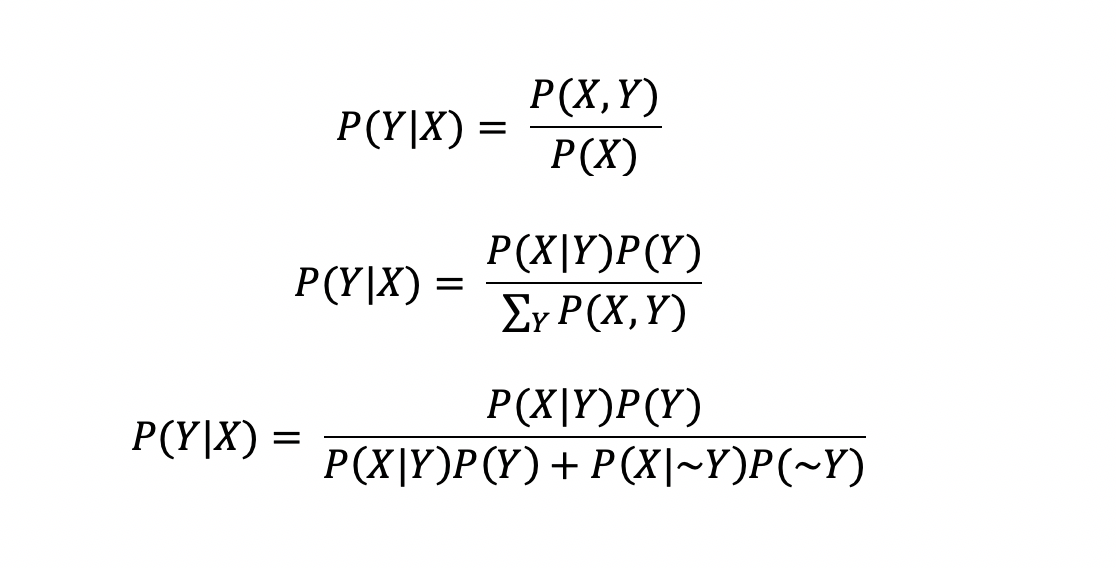



Bayes Theorem Some Perspectives By Garychl Towards Data Science



2




Second Order Linear Differential Equations



2



2




The Graph Of Y P X Where P X Is A Polynomial In Variable X Is As Follows The Number Of Zeroes Of Brainly In




Find P 0 P 1 And P 2 For Each Of The Following Polynomials I P Y Y 2 Y 1 Ii P T 2 T 2t 2 T 3 Iii P X X 3 Iv P X X 1 X 1



2




Distribution Of The Product Of Two Random Variables Wikipedia




Conditional Entropy Wikipedia



Calculating Centers Of Mass And Moments Of Inertia Calculus Volume 3



Lecture 5 Bayes Classifier And Naive Bayes




Value Of A Polynomial Expression Concept Calculator Cuemath



2




The Figure Shows The Graph Of Y P X Number Of Zeroes Of Polynomial



2



2



2
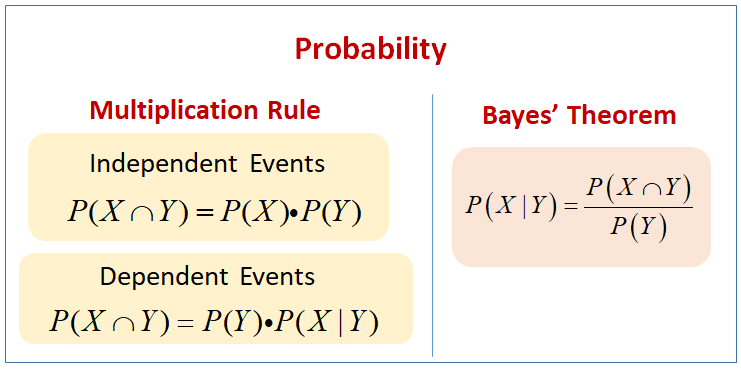



Bayes Theorem Solutions Formulas Examples Videos



173 Lectures



2



2




The Differential Equation Y Px F P I Where P Dy Dx Is Known As Clairout S Equation To Solve Equation I Differentiate It With Respect To X Which Gives Either Dp Dx 0 Rarr P C Ii Or X F I P 0 Iii The Number



2
コメント
コメントを投稿